Last Updated on December 19, 2024 by Michelle Wan
Fetal metabolic acidosis is a serious medical condition that occurs when a baby’s blood becomes too acidic due to insufficient oxygen supply before or during labor. This condition can be a sign of distress, often pointing to complications during pregnancy or delivery. If left untreated, it may lead to long-term health problems or even death.
In this article, we will explore what fetal metabolic acidosis is, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and the potential impact on a child’s health. We’ll also discuss how medical errors during labor and delivery can contribute to this condition.
Understanding Fetal Metabolic Acidosis
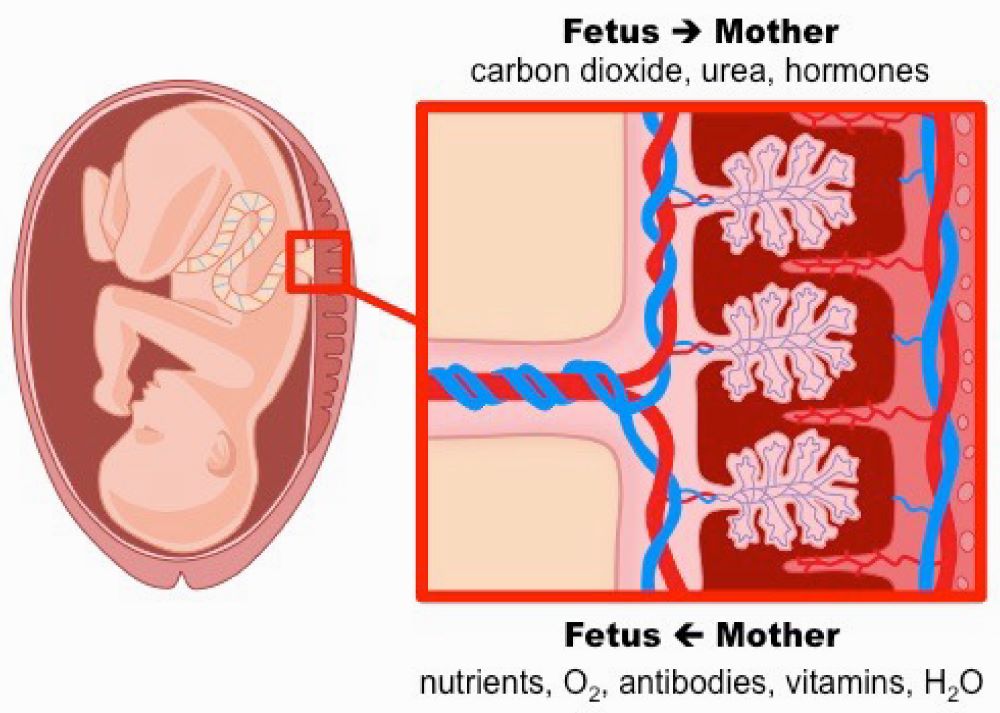
Metabolic acidosis occurs when the body produces excessive amounts of acid or cannot eliminate it effectively, disrupting the normal pH balance of the blood. In fetuses, this imbalance often results from hypoxia (lack of oxygen) and inadequate blood flow to vital organs, including the brain.
Normal Blood pH Levels:
- A healthy blood pH ranges between 7.35 and 7.45.
- Fetal metabolic acidosis is diagnosed when the pH drops below 7.20, indicating excessive acidity.
Causes of Fetal Metabolic Acidosis
Fetal metabolic acidosis typically occurs due to issues that compromise oxygen supply during pregnancy or childbirth. Common causes include:
Placental Insufficiency
When the placenta fails to deliver adequate oxygen and nutrients to the fetus, it can lead to hypoxia and acidosis.
Umbilical Cord Problems
- Cord Prolapse: The umbilical cord slips into the birth canal, cutting off oxygen supply.
- Nuchal Cord: The cord becomes wrapped around the baby’s neck, restricting blood flow.
Prolonged Labor
A lengthy or difficult labor can stress the fetus and reduce oxygen availability.
Maternal Health Conditions
Complications such as preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, or infections can disrupt the baby’s oxygen supply.
Inadequate Monitoring During Labor
Failure to detect and respond to signs of fetal distress, such as abnormal heart rate patterns, can lead to preventable metabolic acidosis.
Symptoms and Signs of Fetal Metabolic Acidosis
Fetal metabolic acidosis is challenging to detect without medical evaluation. However, some warning signs during labor may indicate the need for immediate intervention:
- Abnormal Fetal Heart Rate Patterns: A rapid or slow heartbeat may signal fetal distress.
- Meconium-Stained Amniotic Fluid: This indicates that the baby has passed stool in utero, often a response to oxygen deprivation.
- Reduced Fetal Movement: A decrease in movement may suggest insufficient oxygen.
After birth, babies with metabolic acidosis may display:
- Low Apgar scores.
- Difficulty breathing or requiring resuscitation.
- Seizures or abnormal neurological responses.
Diagnosing Fetal Metabolic Acidosis
Accurate diagnosis of fetal metabolic acidosis requires prompt medical evaluation. Tests used to confirm the condition include:
Umbilical Cord Blood Gas Analysis
Blood taken from the umbilical cord immediately after birth measures pH, oxygen, and carbon dioxide levels to assess acidosis.
Fetal Scalp Blood Sampling
During labor, a small sample of blood from the baby’s scalp can help detect abnormal pH levels.
Continuous Fetal Monitoring
Monitoring the baby’s heart rate during labor can indicate stress or oxygen deprivation.
Treatment of Fetal Metabolic Acidosis
Early intervention is critical to minimize the risk of long-term complications. Treatment strategies include:
Addressing Oxygen Deprivation
- Emergency Delivery: If fetal distress is detected, a cesarean section may be performed to ensure the baby receives adequate oxygen.
- Resuscitation: Babies with severe acidosis may require immediate resuscitation after birth.
Therapeutic Hypothermia
This treatment involves cooling the baby’s body to reduce inflammation and prevent further brain damage, especially in cases of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE).
Supportive Care
Neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) provide advanced monitoring, oxygen therapy, and medications to stabilize the baby’s condition.
Potential Complications of Fetal Metabolic Acidosis
If untreated or improperly managed, fetal metabolic acidosis can result in severe complications, including:
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE): A brain injury caused by oxygen deprivation.
- Cerebral Palsy: Motor and developmental impairments resulting from brain damage.
- Seizure Disorders: Neurological complications due to brain injury.
- Developmental Delays: Challenges with learning, speech, and motor skills.
Medical Negligence and Fetal Metabolic Acidosis
In many cases, fetal metabolic acidosis is preventable with proper medical care. Negligence during pregnancy or delivery may contribute to the condition. Common examples of medical errors include:
- Failure to monitor fetal distress.
- Delays in performing a necessary cesarean section.
- Mismanagement of maternal complications, such as preeclampsia or gestational diabetes.
- Inadequate training or failure to follow established protocols.

If you suspect that medical negligence contributed to your child’s condition, you may have legal recourse to seek compensation for medical expenses, therapies, and future care.
Seeking Legal Support
Families affected by fetal metabolic acidosis face significant emotional and financial burdens. Pursuing a medical malpractice claim can provide compensation to cover:
- Immediate and long-term medical care.
- Therapy costs, such as physical, occupational, and speech therapy.
- Adaptive equipment and home modifications.
- Lost income due to caregiving responsibilities.
At Thomas & Wan LLP, our experienced birth injury attorneys are dedicated to helping families navigate the complexities of medical malpractice claims. We work with medical experts to identify negligence, build a strong case, and secure the resources your child needs.
Fetal metabolic acidosis is a serious condition with potentially lifelong consequences, but timely intervention and proper medical care can significantly improve outcomes. Understanding the causes, recognizing the signs, and seeking appropriate treatment are critical steps for families navigating this challenging diagnosis.
If you believe medical negligence played a role in your child’s condition, contact Thomas & Wan LLP today for a free consultation. Our compassionate team is here to support your family every step of the way.




