Last Updated on November 26, 2024 by Michelle Wan
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of neurological disorders that affect movement, muscle tone, and posture. It occurs due to damage or abnormalities in the developing brain, often before or during birth. While all forms of cerebral palsy share challenges in mobility and coordination, the condition is categorized into distinct types based on the area of the brain affected and the nature of the symptoms.
In this article, we’ll explore the main types of cerebral palsy, their causes, symptoms, and how they impact individuals differently.
What is Cerebral Palsy?
Cerebral palsy is a lifelong condition that affects a person’s ability to move and maintain balance and posture. It is caused by brain damage or abnormalities during early development, typically due to factors such as:
- Lack of oxygen to the brain during birth (birth asphyxia).
- Premature birth or low birth weight.
- Maternal infections or medical conditions during pregnancy.
- Trauma to the head during early infancy.
The severity of symptoms varies widely, ranging from mild motor difficulties to severe physical and intellectual impairments.
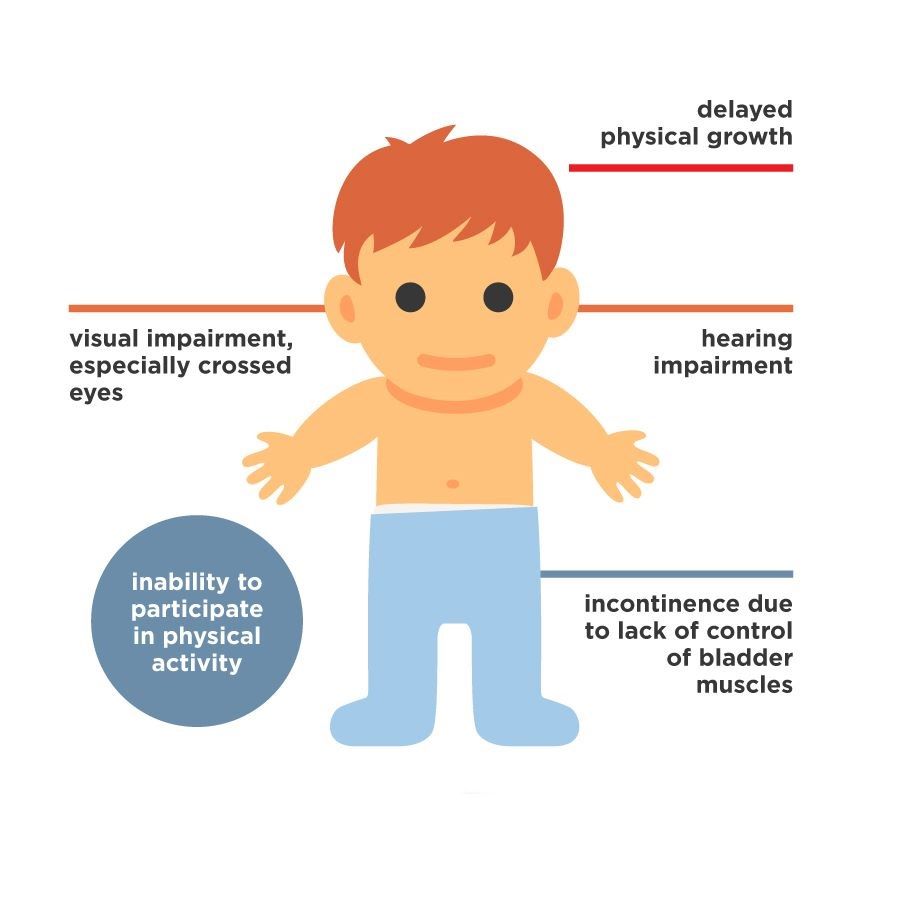
The Four Main Types of Cerebral Palsy
Cerebral palsy is classified into four main types of CP, depending on the affected areas of the brain and the symptoms exhibited.
Spastic Cerebral Palsy
Overview: Spastic cerebral palsy is the most common type, affecting approximately 70–80% of individuals with CP. It is characterized by increased muscle tone (hypertonia), leading to stiffness and difficulty with movement.
Symptoms:
- Tight, stiff muscles that can make movement difficult.
- Difficulty with fine motor skills, such as grasping objects or writing.
- Joint contractures (permanently shortened muscles or tendons).

Subtypes:
- Spastic Diplegia: Affects primarily the legs, causing difficulty walking or standing. Arm movements are less impacted.
- Spastic Hemiplegia: Affects one side of the body (e.g., the right arm and leg), often leading to delayed motor development on that side.
- Spastic Quadriplegia: The most severe form, affecting all four limbs, the torso, and the face. Individuals may also experience seizures, intellectual disabilities, or difficulties with speech.
Impact
Individuals with spastic CP often require physical therapy, medications to manage muscle spasticity, and assistive devices like braces or wheelchairs to improve mobility.
Dyskinetic Cerebral Palsy
Overview: Dyskinetic CP, also called athetoid CP, involves involuntary movements caused by damage to the basal ganglia, the part of the brain responsible for controlling movement.
Symptoms:
- Involuntary, uncontrollable movements (e.g., writhing, twisting, or jerking motions).
- Difficulty maintaining posture and balance.
- Fluctuating muscle tone, shifting between too tight and too loose.
- Challenges with speech and swallowing due to facial muscle involvement.
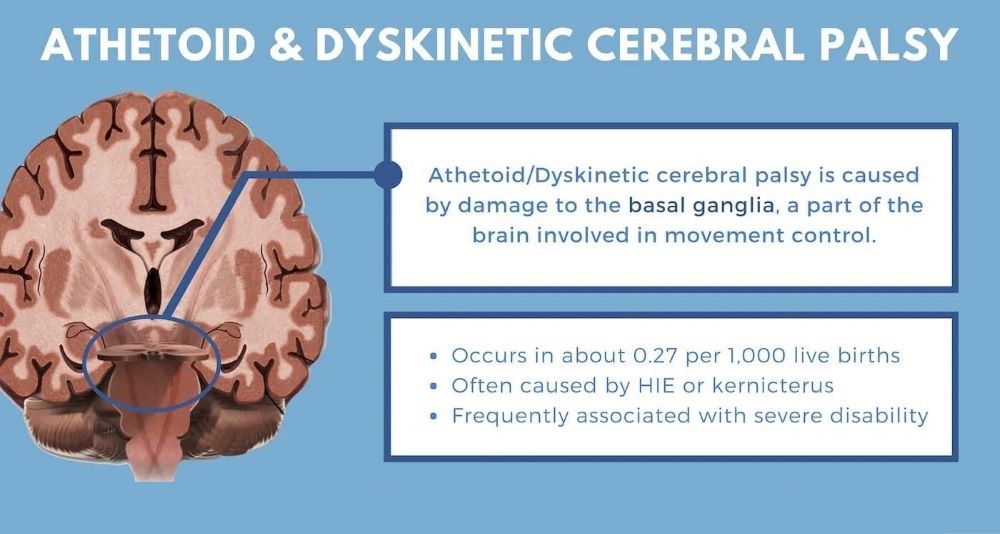
Impact
Dyskinetic CP can make daily tasks like eating, dressing, and writing challenging. Speech therapy and occupational therapy are often recommended to improve communication and fine motor skills.
Ataxic Cerebral Palsy
Overview: Ataxic CP is the least common type, affecting about 5–10% of individuals with CP. It results from damage to the cerebellum, the part of the brain that controls balance and coordination.
Symptoms:
- Difficulty with balance and coordination.
- Tremors or shaky movements when performing tasks.
- Challenges with precise movements, such as writing or buttoning a shirt.
- A wide, unsteady gait when walking.
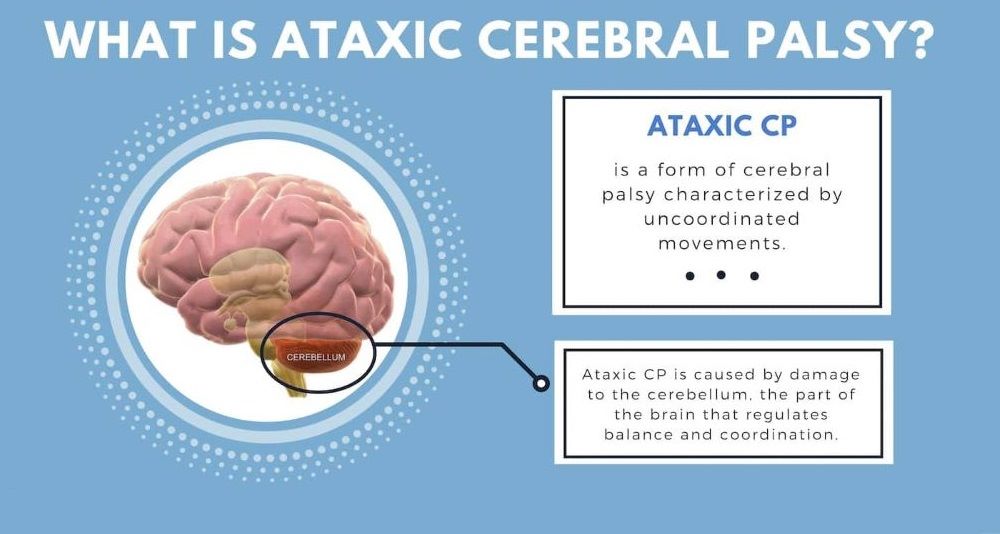
Impact
Ataxic CP primarily affects coordination and fine motor skills. Physical therapy and adaptive devices can help individuals improve balance and mobility.
Mixed Cerebral Palsy
Overview: Mixed CP occurs when an individual exhibits symptoms of more than one type of cerebral palsy. For example, a person may have a combination of spastic and dyskinetic CP.
Symptoms:
- A blend of symptoms from the other types, depending on the specific brain regions affected.
- Muscle stiffness in some areas and involuntary movements in others.
Impact
Treatment for mixed CP often involves a multidisciplinary approach, including physical therapy, medications, and assistive devices to address the diverse range of symptoms.
How Cerebral Palsy is Diagnosed
Diagnosis typically involves:
- Developmental Monitoring: Regular check-ups to observe milestones like crawling, sitting, and walking.
- Imaging Tests: MRI or CT scans to identify brain damage or abnormalities.
- Neurological Exams: Assessing muscle tone, reflexes, and coordination.
Early diagnosis is crucial for developing a tailored treatment plan and accessing supportive resources.

Treatment and Support Options for Cerebral Palsy
While there is no cure for cerebral palsy, various treatments and therapies can help improve quality of life:
- Physical Therapy: Enhances strength, balance, and motor skills.
- Occupational Therapy: Develops skills for daily activities, such as eating or dressing.
- Speech Therapy: Improves communication abilities and addresses feeding challenges.
- Medications: Reduces muscle stiffness or involuntary movements.
- Assistive Devices: Includes wheelchairs, braces, and communication aids.
- Surgical Interventions: In severe cases, surgery can address muscle tightness or skeletal abnormalities.
Supporting Families Affected by Cerebral Palsy
Caring for a child with cerebral palsy can be emotionally and financially demanding. Families often face significant expenses related to medical care, therapies, and adaptive equipment. Resources are available to help ease these burdens:
- Nonprofit Organizations: A National institute like United Cerebral Palsy (UCP) provides financial aid, advocacy, and community support.
- Government Programs: Medicaid and Supplemental Security Income (SSI) can help cover therapy and equipment costs.
- Legal Compensation: If cerebral palsy resulted from medical negligence, families may pursue compensation to cover care and therapy costs.
Understanding the different types of cerebral palsy helps families and caregivers better support individuals with the condition. Each type presents unique challenges, but with early intervention, tailored therapies, and the right resources, individuals with cerebral palsy can lead fulfilling lives.
If your child’s cerebral palsy was caused by medical negligence, Thomas & Wan LLP is here to help you secure the justice and compensation your family deserves. Contact us today for a session to discuss your case and learn how we can support your journey.




